
Tải ngay bộ hình nền cực chill cho điện thoại và máy tính
Tải bộ hình nền chill nhiều chủ đề, phong cách khác nhau trên máy tính và điện thoại. Bật mí cách tải hình nền chill từ Google chất lượng sắc nét. Xem ngay bài viết!
Bạn muốn tải hình nền chill nhiều chủ đề trầm buồn, phong cảnh, anime, lofi chất lượng 4K cho điện thoại và máy tính của mình. Vậy thì hãy cũng theo dõi bộ sưu tập ảnh nền cực chill ngày hôm nay để tìm cho mình ảnh nền ưng ý nhất nhé!

Tổng hợp hình nền chill cho điện thoại
Những bức hình nền chill sâu lắng tĩnh lặng sẽ mang lại cho bạn cảm giác thư thái nhẹ nhàng. Cũng như mang lại giá trị thẩm mỹ cho điện thoại của bạn. Mời các bạn cũng theo dõi một số ảnh nền chill theo chủ đề cho điện thoại sau đây:
Hình nền phong cảnh cực chill
Ảnh nền phong cảnh chill cho bạn cảm giác như đang lạc trong một kỳ nghỉ ngắn hạn. Là liều thuốc tinh thần giúp bạn phần nào xua tan đi những căng thẳng mệt mỏi.
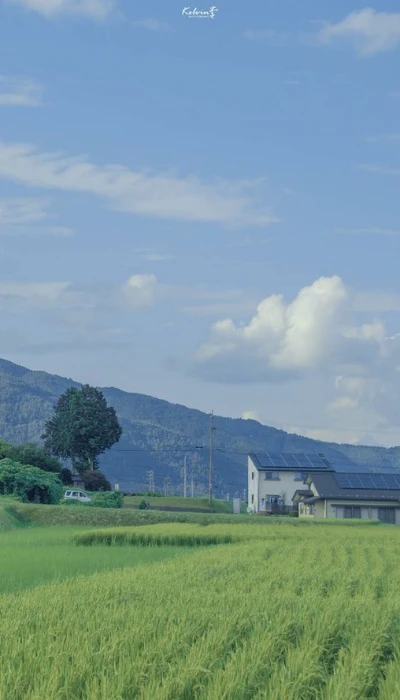
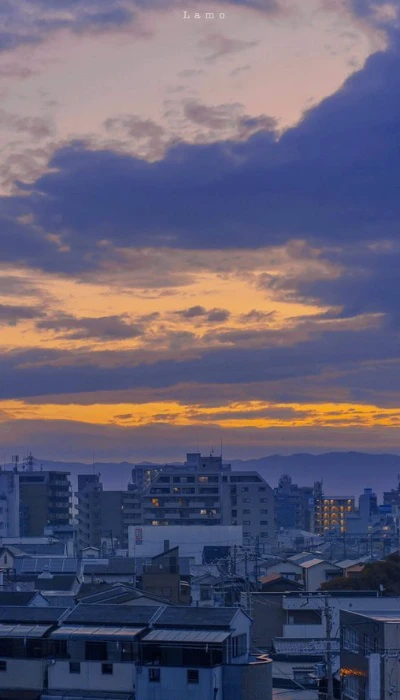
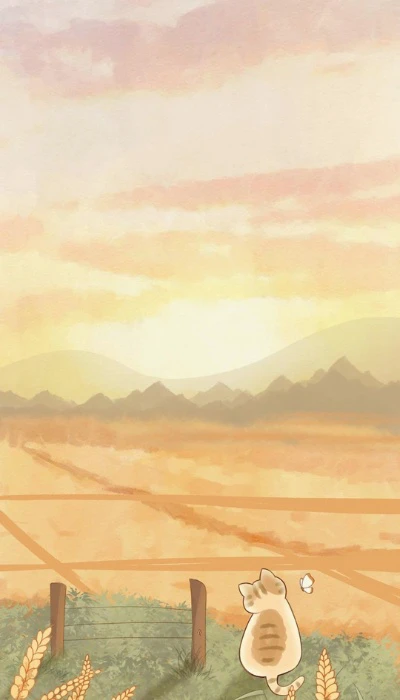
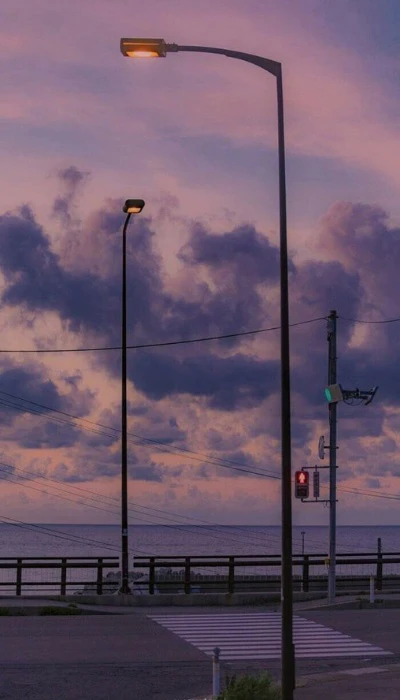
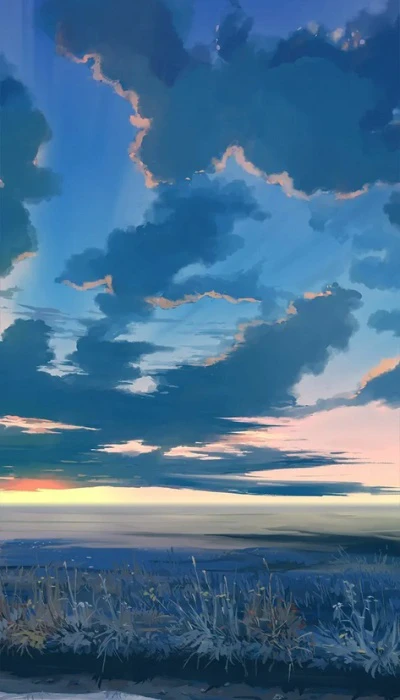






Tải ngay bộ ảnh nền phong cảnh cực chill về điện thoại tại đường link: https://s.net.vn/nP8J
Hình nền chill buồn
Bộ ảnh nền chill buồn dành cho người tâm trạng, mang lại cảm giác trầm tư, sâu lắng.
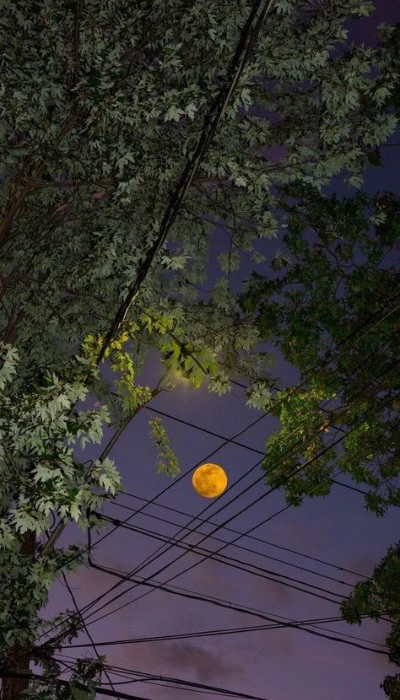
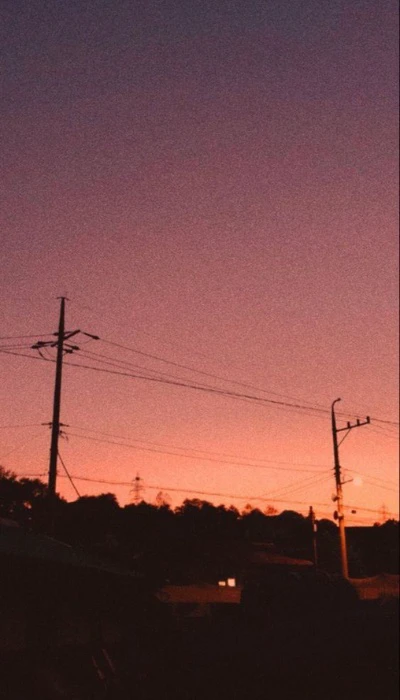
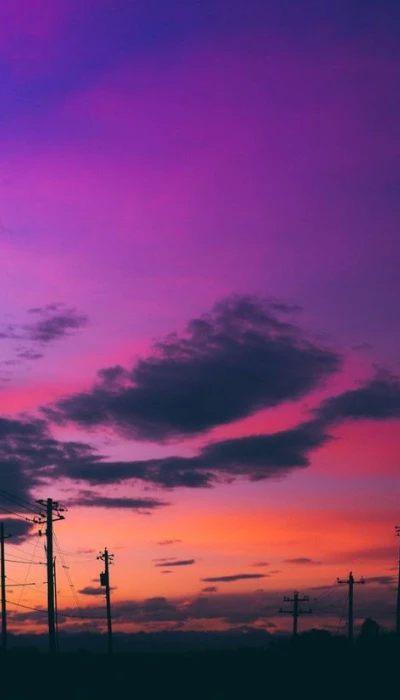






Để tải ảnh chất lượng hơn, bạn hãy vào đường link dưới đây: https://s.net.vn/s1D2
Hình nền Luffy Gear 5 fan anime không thể bỏ qua, xem ngay!
Hình nền chill 4K
Bạn đang tìm kiếm hình nền cực chill chất lượng 4K sắc nét cho màn hình điện thoại của mình. Vậy thì mời các bạn cùng xem bộ sưu tập ảnh sau đây:






Lưu ảnh nền chill 4K sắc nét tại link sau: https://s.net.vn/3AP8
Hình nền chill anime
Là một fan cuồng của phim hoạt hình Nhật Bản nhưng lại mang một tâm hồn sâu lắng nhẹ nhàng. Thì bộ hình nền chill anime rất phù hợp với bạn.
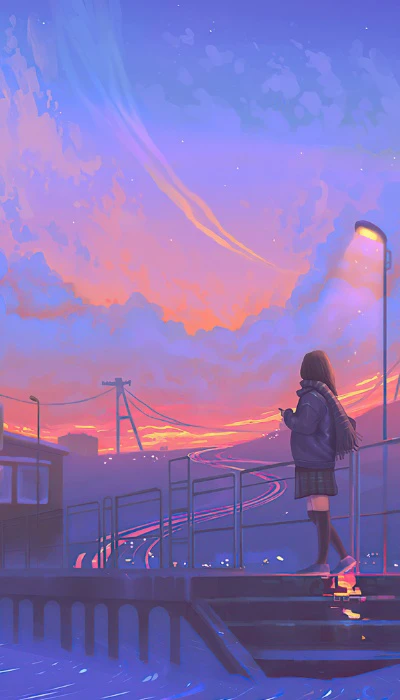
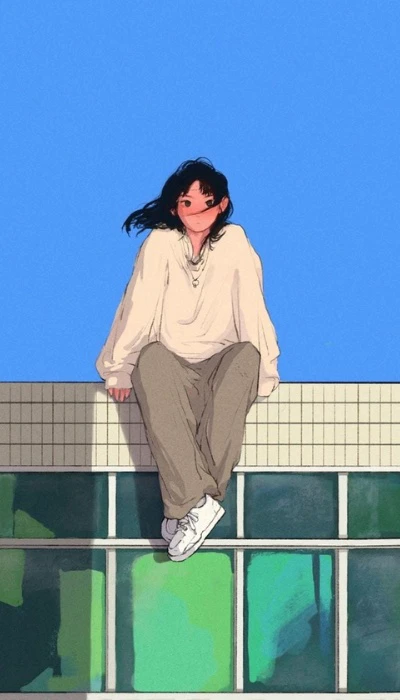
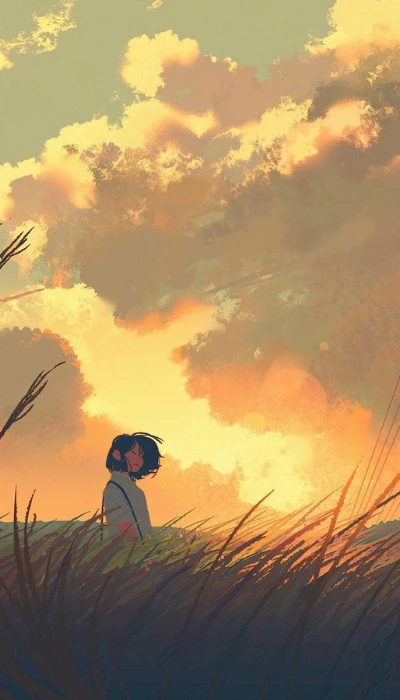
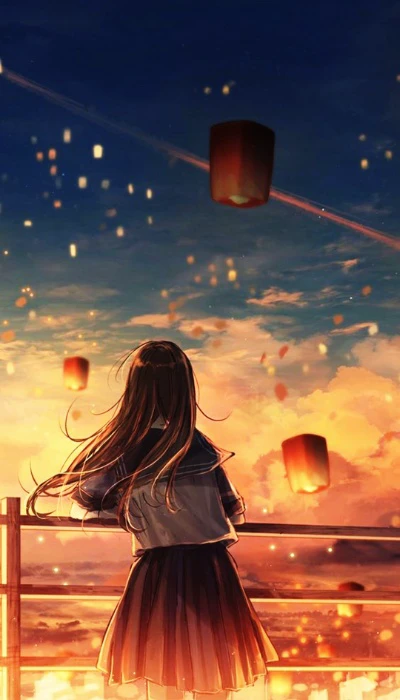






Bạn có thể tải bộ ảnh nền chill anime bằng link sau: https://s.net.vn/a2GA
Ảnh nền chill đẹp
Là người yêu thiên nhiên, mây trời, vũ trụ, sóng biển... Bạn có thể tải ngay bộ ảnh nền chill cực đẹp về thiên nhiên ngay dưới đây:
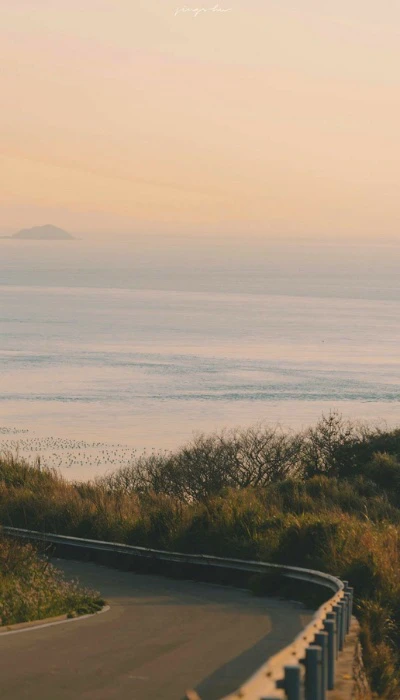
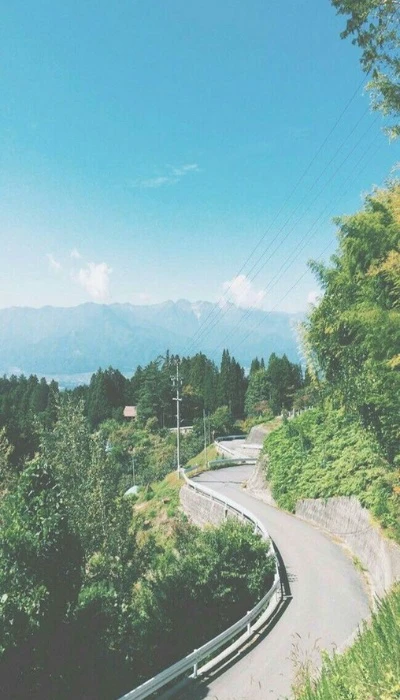
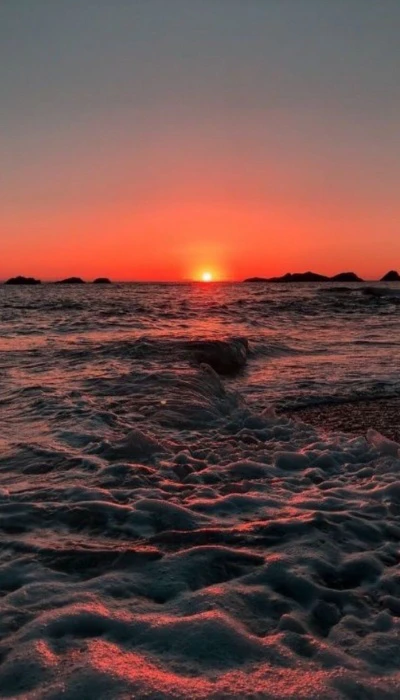






Tải ảnh nền chill đẹp chất lượng cao tại đây: https://s.net.vn/nLsC
Wallpaper chill cute
Với bạn nữ yêu thích sự dễ thương, ảnh nền chill cute cho điện thoại sẽ khiến bạn yêu thích.
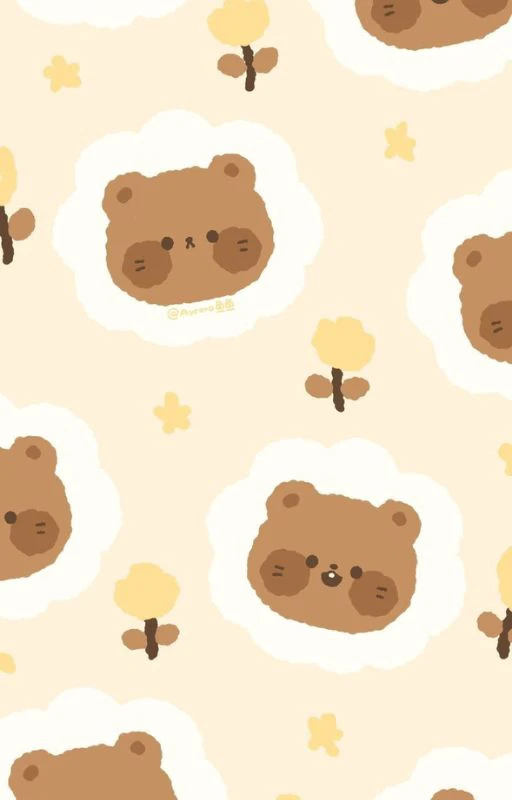





.jpg)


Để tải bộ ảnh nền chill cute trên hãy truy cập đường link: https://s.net.vn/nR3R
Ảnh nền chill hoa đẹp
Wallpaper chill hoa với nhiều màu sắc tươi tắn sẽ giúp màn hình điện thoại sống động hơn. Hãy cùng lựa chọn một tấm ảnh nền trong bộ ảnh nền chill hoa đẹp dưới đây nhé!
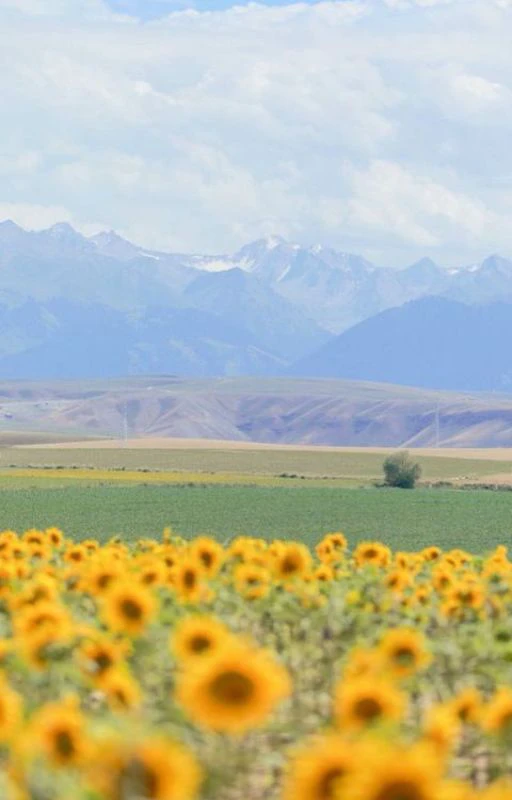
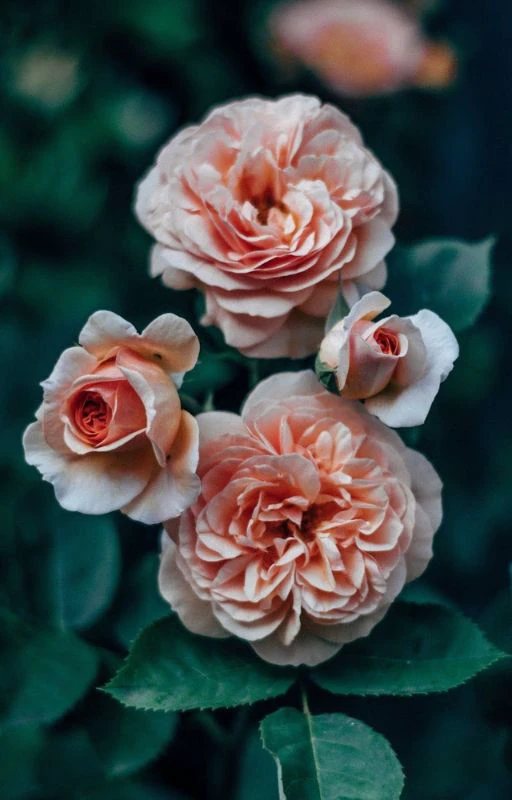








Bạn vào link sau để tải ảnh nền hoa đẹp nhé: https://s.net.vn/pAyc
Hình nền chill bầu trời
Ảnh nền với bầu trời thơ mộng giúp bạn cảm thấy thư thái hơn khi nhìn vào điện thoại. Hãy cùng tham khảo bộ hình nền chill bầu trời dưới đây!
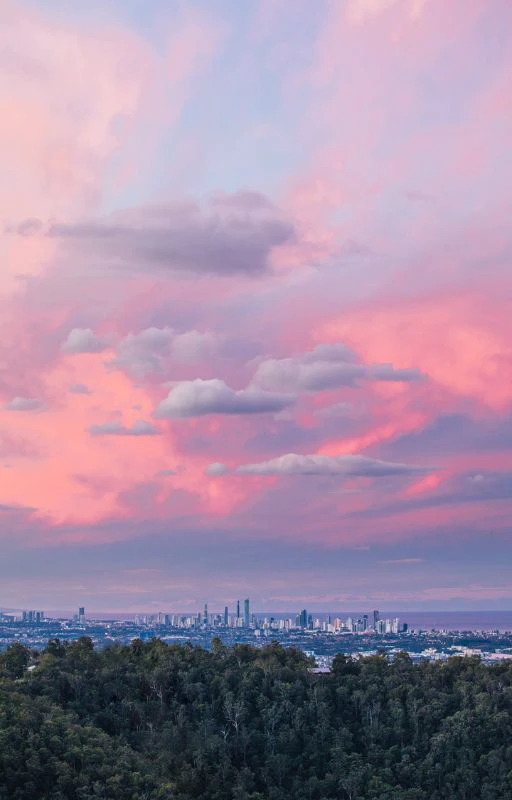
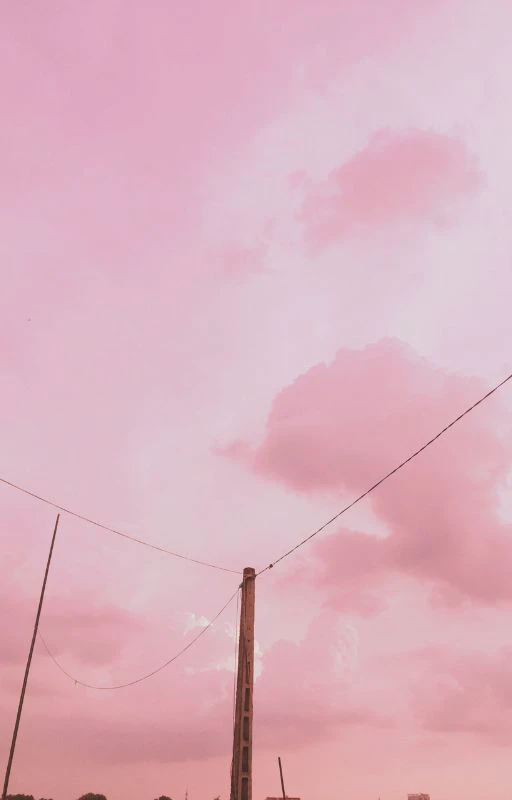
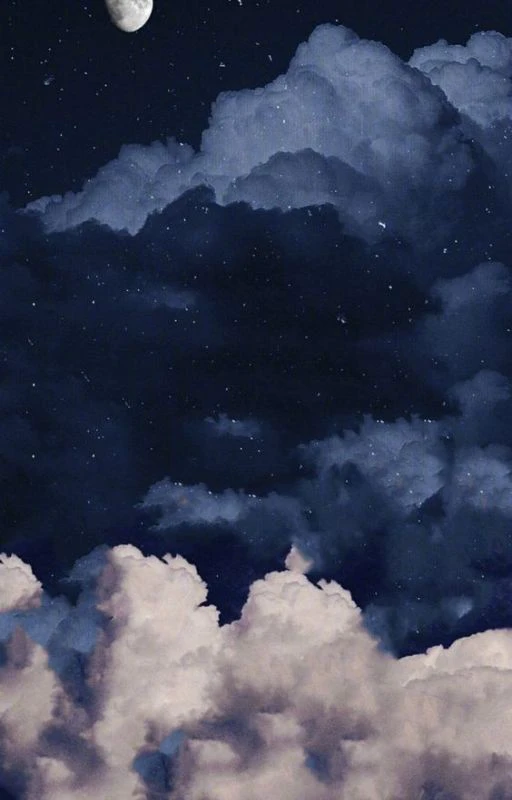








Tải hình nền chill bầu trời sắc nét tại đây: https://s.net.vn/loiZ
Ảnh nền chill học tập
Khi cần tạo hứng thú học tập, bạn có thế lựa chọn một wallpaper chill học tập trong bộ ảnh dưới đây.
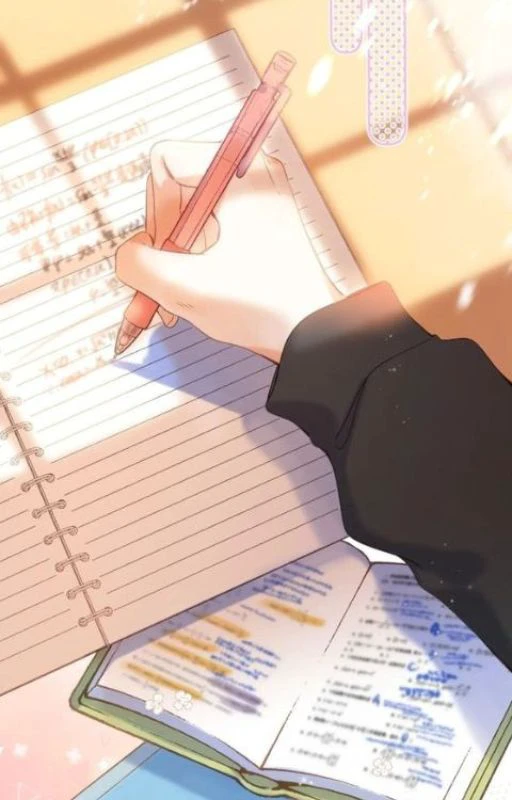
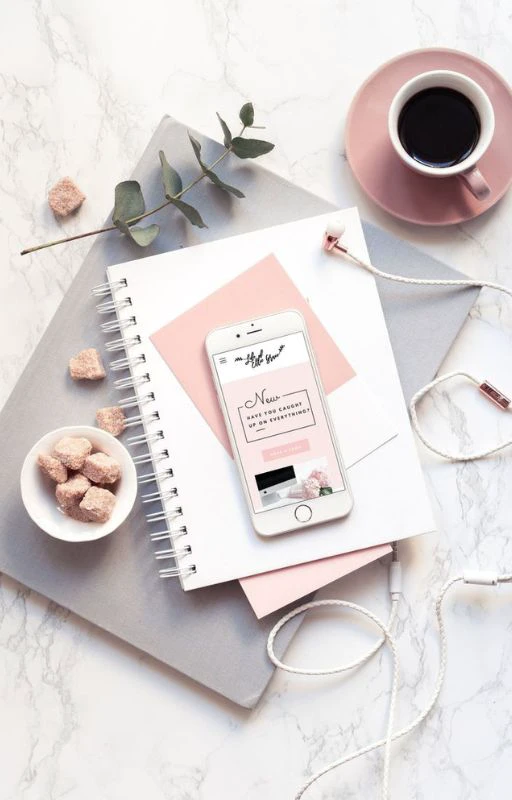
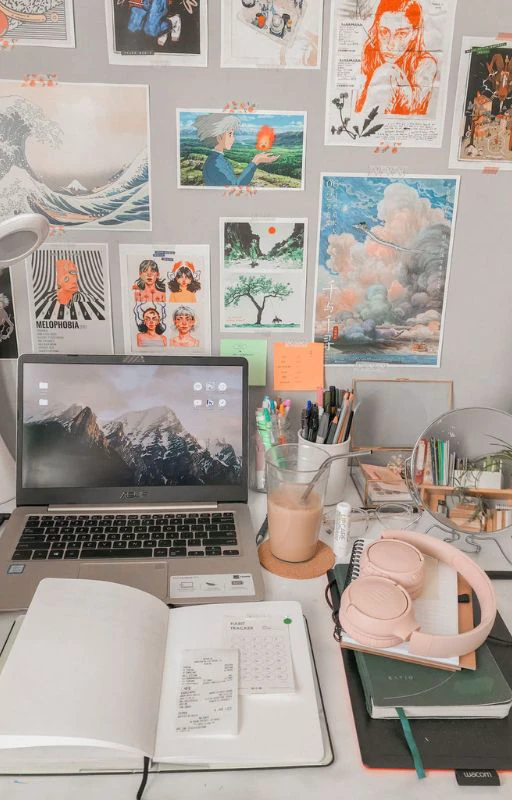








Để lưu ảnh nền chill học tập, bạn có thể tải tại link sau: https://s.net.vn/5uTo
Hình nền chill phi hành gia
Wallpaper chill phi hành gia phù hợp cho những bạn yêu thích không gian vũ trụ. Bạn có thể tham khảo bộ ảnh nền chill phi hành gia cực nét sau đây.


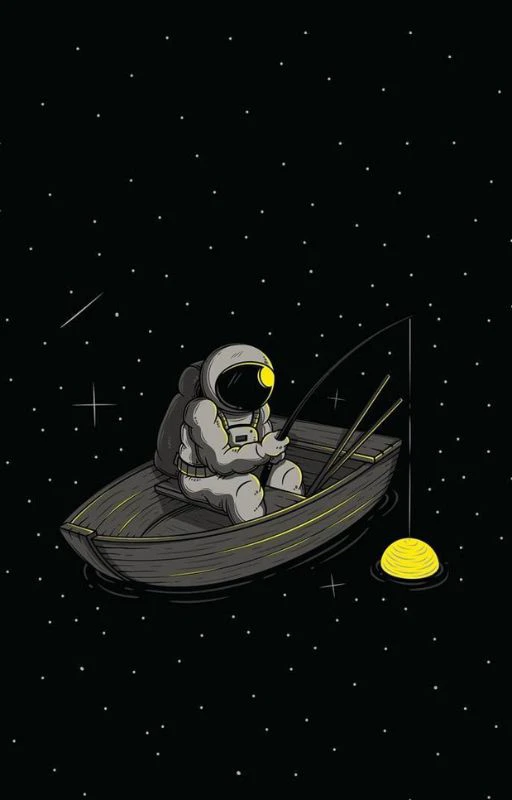





Tải hình nền phi hành gia sắc nét để đặt làm hình nền tại đây: https://s.net.vn/4w2p
Wallpaper chill lofi
Đối với các bạn yêu thích phong cách lofi nhẹ nhàng trầm lắng để thư giãn. Tổng hợp ảnh nền chill lofi dưới đây sẽ thích hợp cho bạn đấy nhé.








Để tải wallpaper chill lofi gốc, bạn có thể vào link sau: https://s.net.vn/QhFo
Cách cài hình nền trên điện thoại
Đã tìm được ảnh nền ưng ý, nhưng bạn chưa biết cài ảnh nền ấy vào điện thoại như thế nào? Vậy thì hãy cùng theo dõi hướng dẫn sau đây:
Cài hình nền điện thoại trên iPhone:
- Bước 1: Mở Bộ sưu tập (Album) và chọn bức ảnh muốn cài làm hình nền.
- Bước 2: Click vào biểu tượng Tùy chọn, sau đó chọn Dùng làm hình nền.
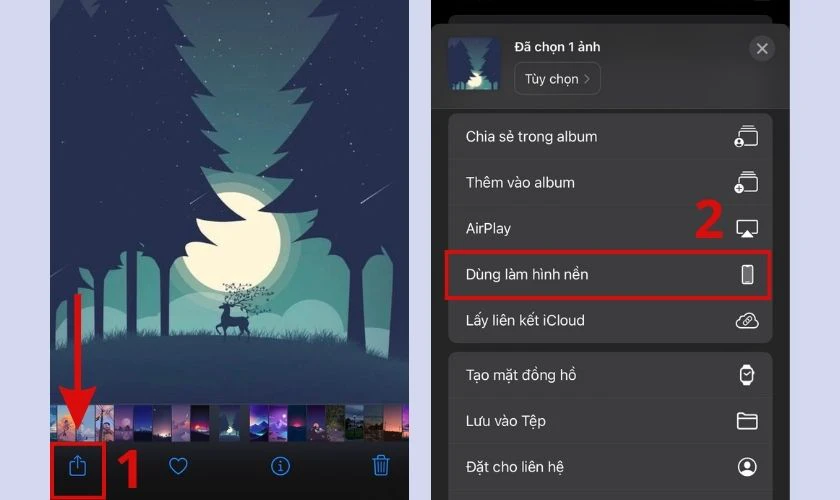
- Bước 3: Chọn Xong và click vào Đặt cặp làm hình nền để hoàn tất.
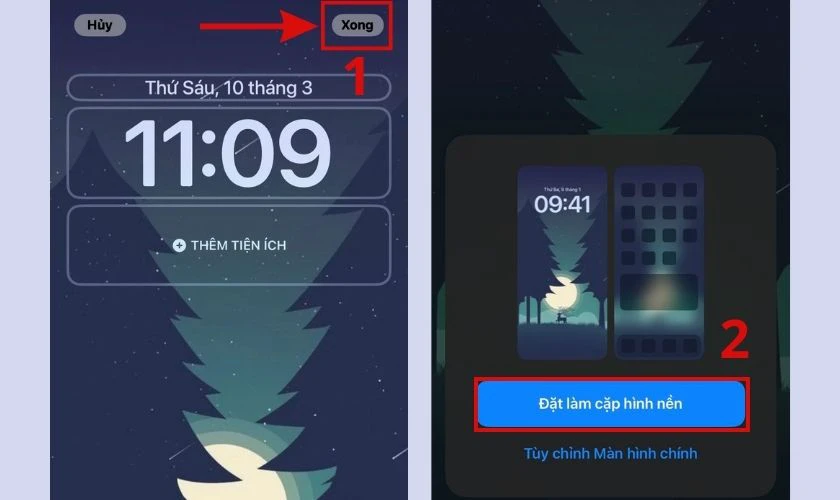
Cài hình nền trên điện thoại Android:
- Bước 1: Truy cập vào Bộ sưu tập (Album ảnh), chọn bức ảnh muốn cài làm ảnh nền.
- Bước 2: Click vào biểu tượng ba chấm (Khác), sau đó chọn Đặt làm hình nền.
- Bước 3: Cuối cùng chọn Áp dụng để hoàn tất.
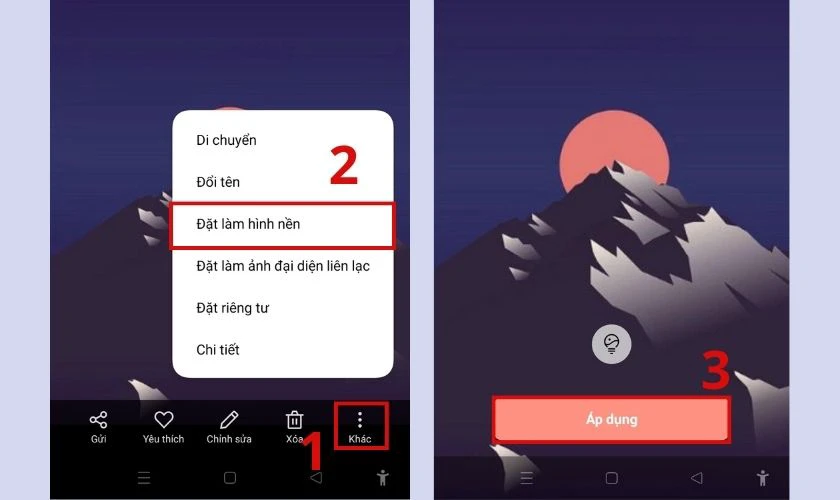
Lưu ý: Bạn nên lên link Drive để tải được ảnh chất lượng nhất nhé!
Xem thêm các thủ thuật hay khác tại website Điện Thoại Vui nhé!
Tổng hợp hình nền máy tính cực chill rõ nét nhất
Bạn đang muốn tải bộ ảnh nền chill máy tính cho PC, laptop của mình. Bạn muốn có một ảnh nền thực sự thư giản thoải mái? Hãy cũng theo dõi bộ sưu tập wallpaper cực chill dưới đây:
Ảnh nền máy tính chill 4K
Tải ngay bộ hình nền máy tính cực chill chất lượng 4K sắc nét về máy ngay dưới đây.






Để tải ảnh nền chill 4K cho máy tính, bạn truy cập link sau: https://s.net.vn/byo5
Hình nền máy tính chill lofi
Hình nền máy tính lofi cực chill cho người yêu thích sự yên tĩnh, thanh bình, nhẹ nhàng.






Bạn có thể tải hình nền máy tính chill lofi tại đây: https://s.net.vn/IUhH
Hình nền máy tính chill lấp lánh
Bạn đang muốn tìm một ảnh nền lấp lánh vừa chill và sang chảnh. Cùng theo dõi bộ ảnh này nhé!


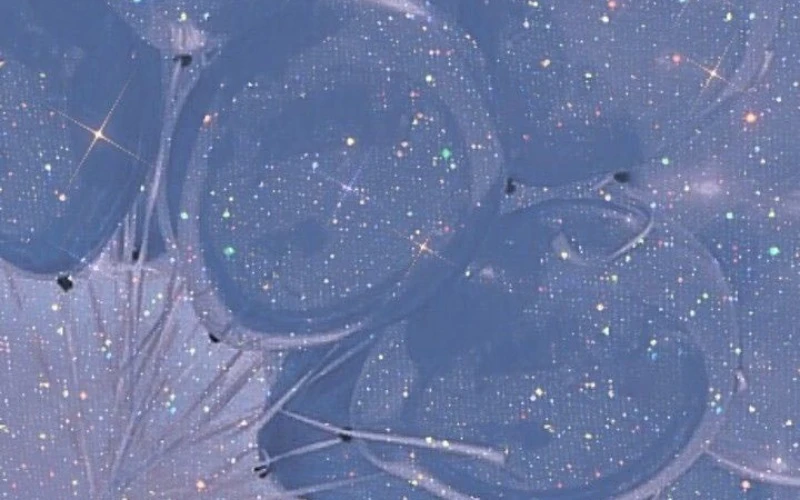



Tải trọn bộ ảnh nền chill lấp lánh tại đây: https://s.net.vn/UZjx
Wallpaper chill hoa đẹp
Bộ hình nền chill hoa nhiều màu sắc sẽ phù hợp với các bạn yêu thích thiên nhiên hoa cỏ.








Bộ ảnh nền chill hoa gốc để cài đặt cho máy tính tại đây: https://s.net.vn/f8LK
Ảnh nền chill bầu trời
Ảnh nền chill bầu trời đặc biệt phù hợp với các bạn yêu thích sự thư thái, nhẹ nhàng yên bình. Bộ sưu tập wallpaper dưới đây sẽ giúp bạn cảm thấy thoải mái hơn khi nhìn vào màn hình máy tính.








Tải ảnh nền chill bầu trời chất lượng sắc nét tại đây: https://s.net.vn/P0Uw
Hình nền chill học tập
Ảnh nền chill học tập cho máy tính sẽ dành cho các bạn cần sự chăm chỉ. Đặc biệt wallpaper này sẽ giúp bạn có thêm động lực học tập khi ngồi vào bàn làm việc.
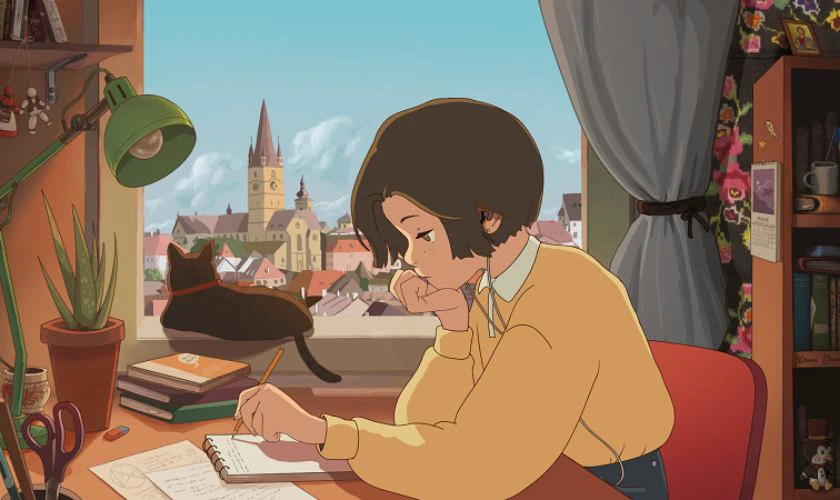
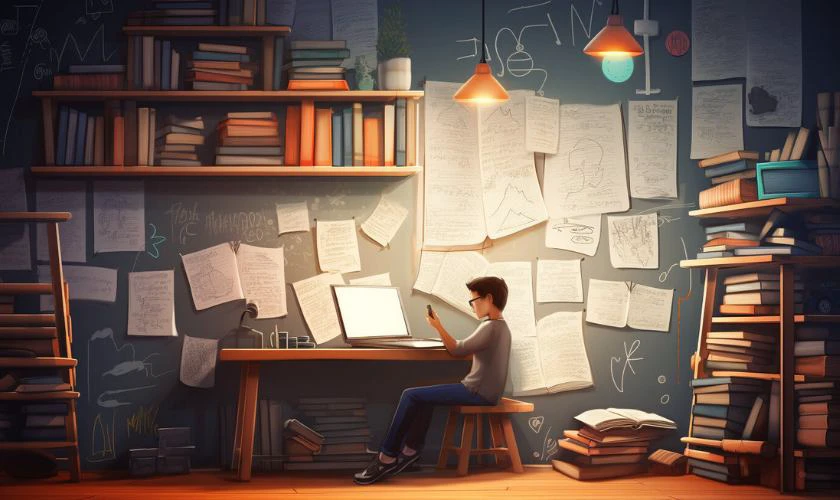
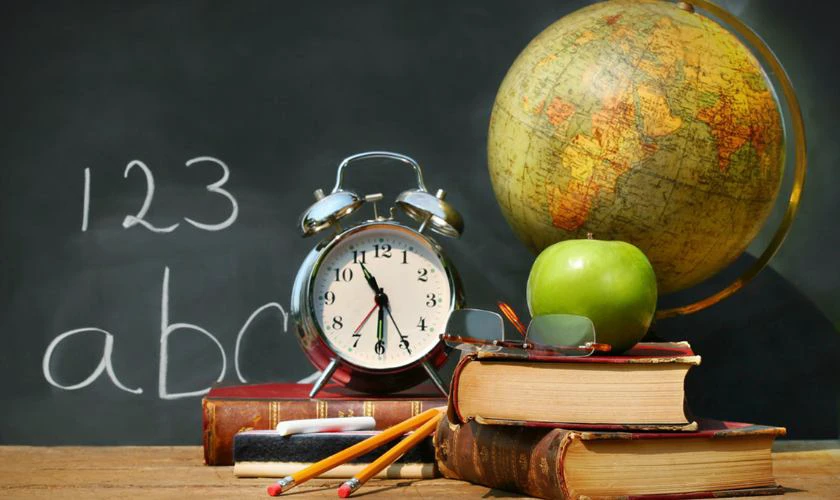








Nhấn vào link dưới đây để tải wallpaper chill học tập: https://s.net.vn/PHdd
Wallpaper chill phi hành gia
Ảnh nền chill phi hành gia cho máy tính sẽ phù hợp cho các bạn yêu thích thiên văn học. Bộ sưu tập wallpaper phi hành gia dưới đây sẽ giúp màn hình máy tính trở nên thú vị hơn.
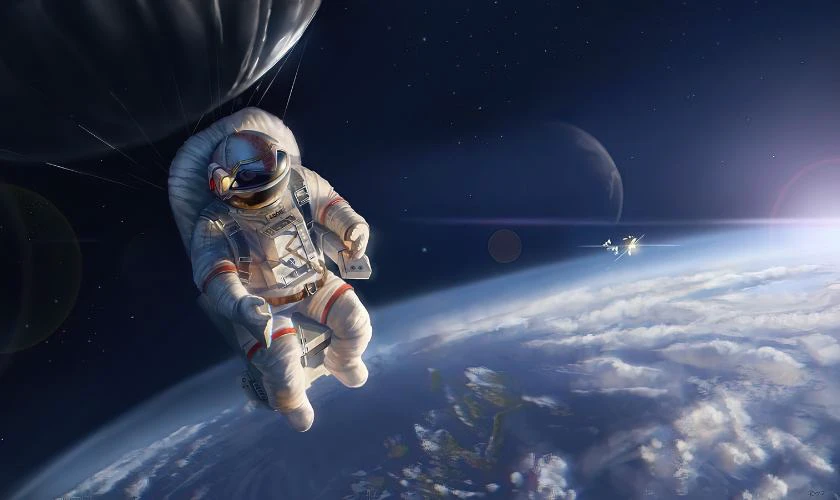
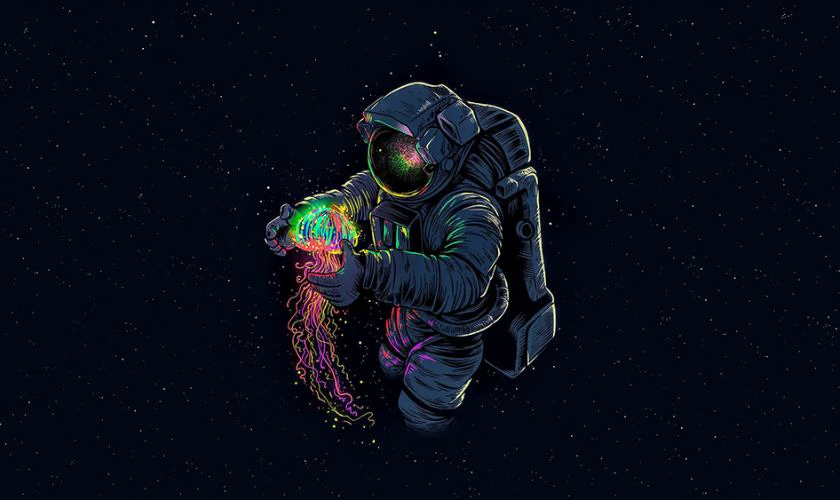
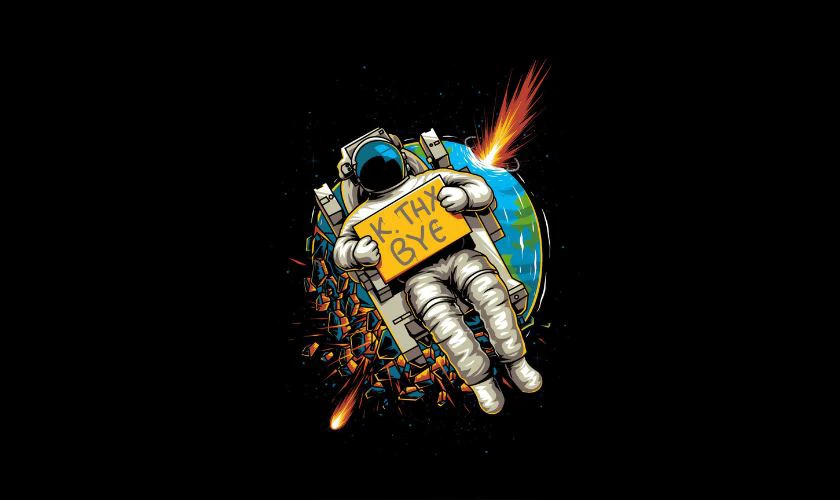
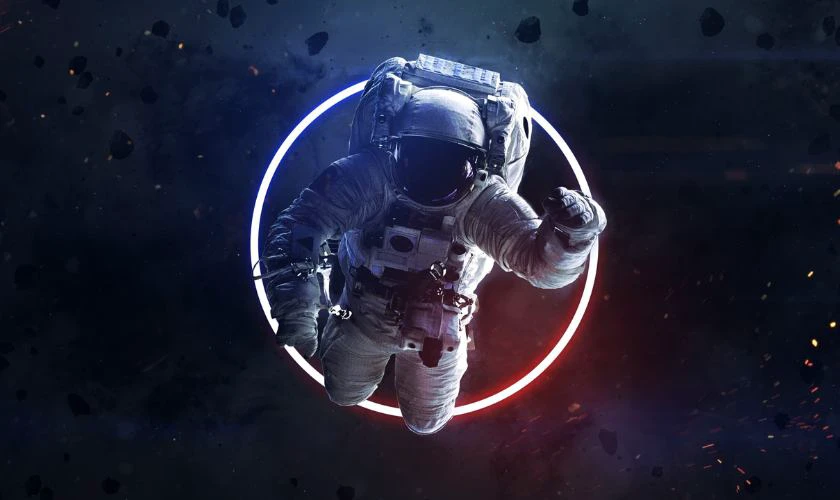
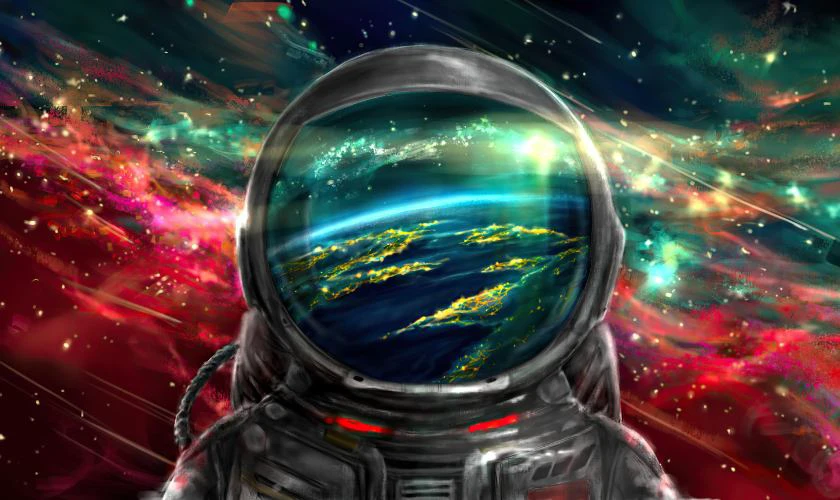








Tải ảnh nền chill phi hành gia rõ nét cho máy tính tại đây: https://s.net.vn/U28u
Cách cài hình nền trên máy tính
Sau khi tải xong ảnh nền, nhưng bạn không biết làm thế nào để thiết lập wallpaper cho máy tính. Bạn có thể theo dõi hướng dẫn ngay bên dưới nhé!
- Bước 1: Mở file ảnh muốn cài đặt lại hình nền.
- Bước 2: Click chuột phải vào ảnh, chọn Set as destop background.
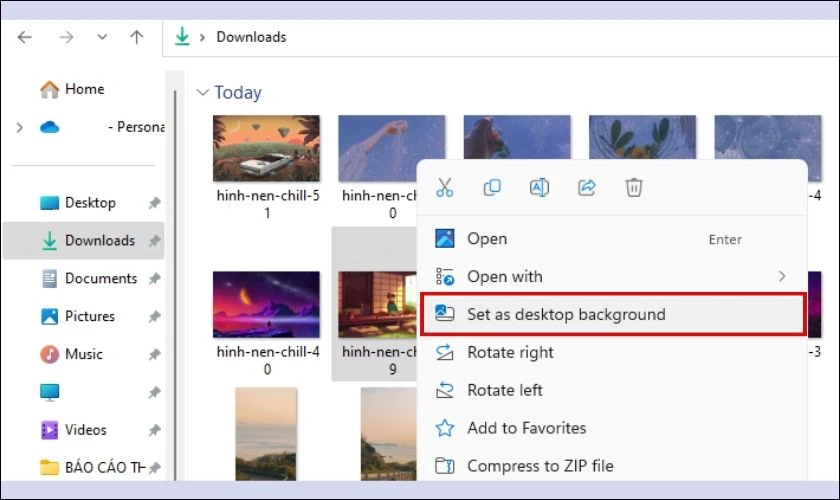
Chỉ với 2 bước đơn giản trên, bạn đã thành công cài đặt ảnh nền chill cho máy tính của bạn.
Xem thêm: Nếu bạn đang có nhu cầu thay pin iPhone chính hãng giá rẻ tại TPHCM và Hà Nội. Đến ngay Điện Thoại Vui, chúng tôi cam kết dịch vụ sửa chữa nhanh chóng với linh kiện chính hãng. Đảm bảo sẽ giúp điện thoại của bạn hoạt động tốt như lúc mới mua. Xem ưu đãi mới nhất tháng 12/2024 ngay tại đây!
[dtv_product_related category='thay-pin/thay-pin-dien-thoai-iphone']
Cách tải ảnh từ Google về máy rõ nét
Như đã đề cập ở trên, để có thể tải ảnh về máy được sắc nét không vỡ ảnh, bạn có thể tải ảnh trực tiếp từ link Drive. Nếu bạn chưa biết cách tải ảnh trên Drive về máy, có thể đọc qua hướng dẫn bên dưới nhé!
- Cách tải ảnh trên máy tính: Mở link Drive, click chuột phải chọn Tải xuống. Ảnh sau khi tải sẽ được lưu tại thư mục Download.
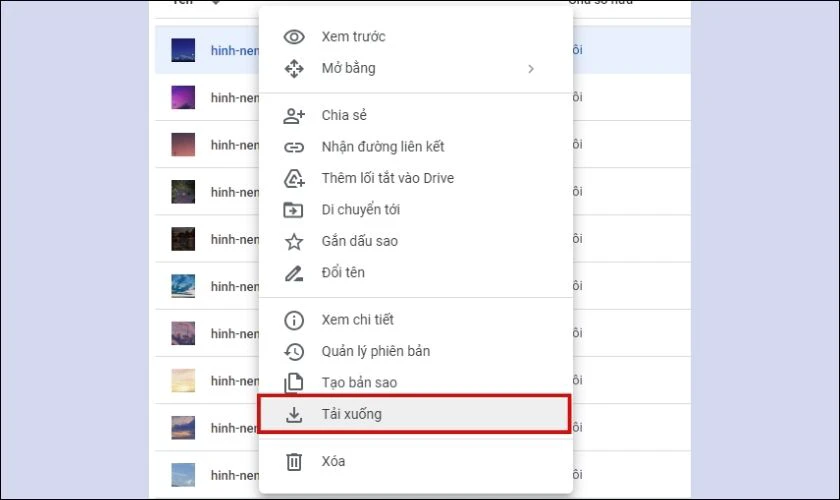
- Cách tải ảnh từ Drive trên điện thoại: Mở link Drive bằng điện thoại. Tại ảnh muốn tải, nhấn giữ đến khi hiện thông báo tải xuống, click chọn OK.
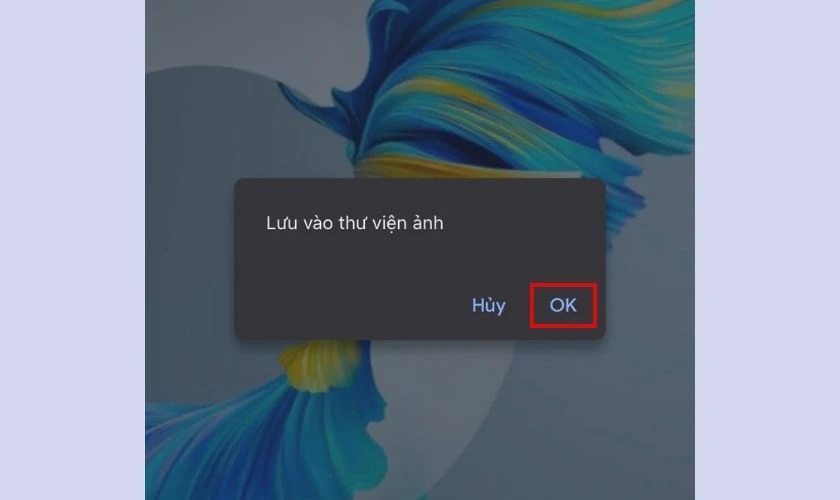
Trên đây là tổng hợp hình nền chill buồn, anime, 4K và nhiều chủ đề khác cho điện thoại và máy tính, chúc các bạn có thể chọn được ảnh nền ưng ý. Đừng quên chia sẻ để nhiều người cùng biết đến bộ sưu tập này nhé! Theo dõi Điện Thoại Vui để không bỏ lỡ các thủ thuật iPhone hữu ích khác bạn nhé!
Bạn đang đọc bài viết Tải ngay bộ hình nền cực chill cho điện thoại và máy tính tại chuyên mục Tin công nghệ trên website Điện Thoại Vui.
Admin
Link nội dung: https://pi-web.eu/tai-ngay-bo-hinh-nen-cuc-chill-cho-dien-thoai-va-may-tinh-1735564548-a1831.html